Top 20 Foods Rich in Niacin
If you are struggling with heart health and cholesterol levels or seem to be getting more tired faster than before, a niacin boost may just be what you need.
Consuming enough niacin is important to your health. Outside of its ability to improve cholesterol and cardiovascular health, it is also important for other functions like the breakdown of carbohydrates into glucose for energy.
Niacin is a water soluble vitamin and is not stored by the body. Therefore, you must make sure that you are getting adequate amounts of it daily from food and supplements
Niacin is more commonly known as vitamin B3 and can be found in a variety of foods.
Dietary Reference Intake (DRI) – Niacin
The dietary reference intake refers to the daily recommended values of niacin for people based on the diet appropriate for their ages.
The World Health organization recommends the following DRI;
- Infants, birth to 6 months: 2 mg (adequate intake)
- Infants, 7 months to 1 year: 4 mg (adequate intake)
- Children, 1 to 3 years: 6 mg (RDA)
- Children, 4 to 8 years: 8 mg (RDA)
- Children, 9 to 13 years: 12 mg (RDA)
- Boys, 14 to 18 years: 16 mg (RDA)
- Girls, 14 to 18 years: 14 mg (RDA)
- Men, 19 years and older: 16 mg (RDA)
- Women, 19 years and older: 14 mg (RDA)
- Pregnant women: 18 mg (RDA)
- Breastfeeding women: 17 mg (RDA)
For people who use niacin as a medication, the upper limit which should never be exceeded are as follows;
- 1-3 years: 10 milligrams
- 4-8 years: 15 milligrams
- 9-13 years: 20 milligrams
- 14-18 years: 30 milligrams
- 19+ years: 35 milligrams
- Pregnant or lactating women, 18 years and younger: 30 milligrams
- Pregnant or lactating women, 19 years and older: 35 milligrams
Do you desire to boost Niacin naturally, improve healthy and fitness life? NIACINMax may help you, check it here.
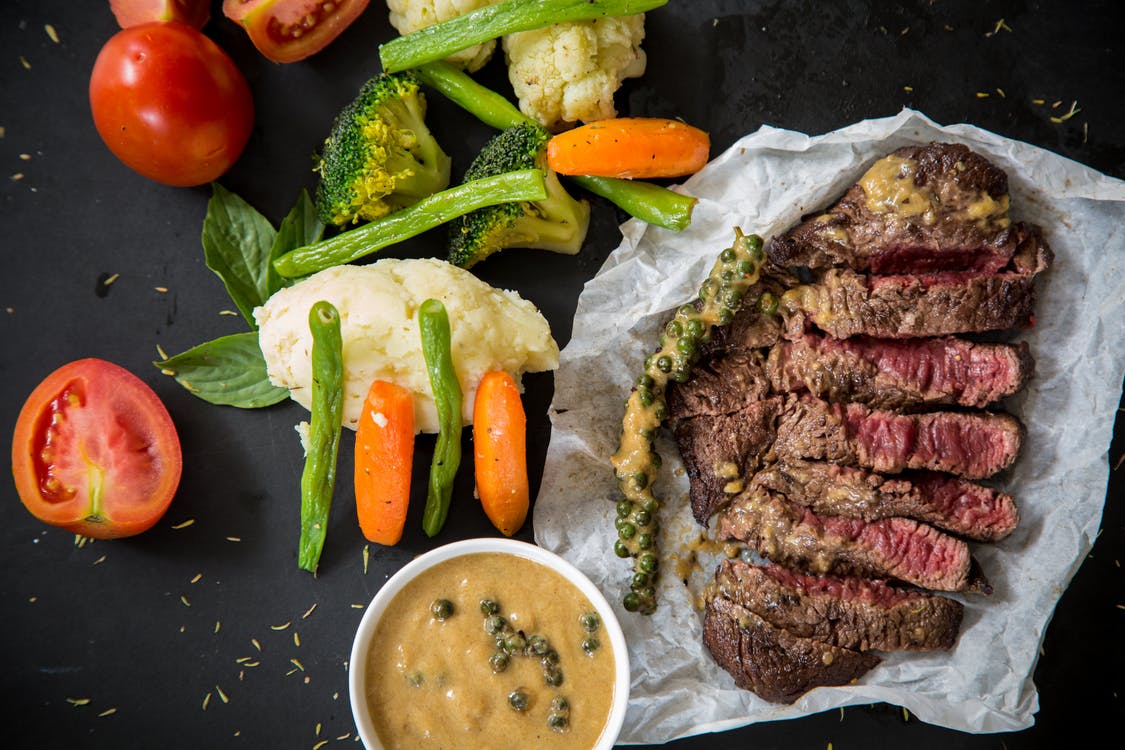
Apart from mushrooms, asparagus and avocadoes, most of the excellent sources of niacin are animal derived foods.
The other major sources of niacin are legumes, root vegetables, nuts and seeds. Many niacin rich foods are a part of our diet already.
Some of the more excellent sources of niacin are;
Poultry (Chicken, Turkey):
Poultry is one of the more amazing sources of vitamin B3. One turkey breast contains over 100% of the daily recommended intake of niacin.
One chicken breast can also provide you a much as 74% of the daily recommendation of niacin.
Nuts and seeds:
Sunflower seeds will provide you with about 19% of your daily niacin needs. A cup of peanuts will provide you with over 100% of the niacin you need daily.
Other nuts such as almonds and pecans will also provide you with a good amount of niacin.
Fish:
Most fish contain some niacin. A serving of tuna will give you about 156% of your recommended niacin intake.
A serving of wild salmon will give you about 43% and a serving of halibut or swordfish will give you a little less than 40%.
Lean meats:
Grass fed beef is a great source of niacin containing about 39% of your daily needs in every 3 ounces you eat of the ribs you eat. Other parts of the meat contain varying amounts of niacin.
The Lean Sirloin Steak has 38% of your niacin needs, Beef Fillet has 37%, and Tenderloin has 36%.
Mushrooms:
Mushrooms are of several types. Some of them are edible while others are not. One cup of Portobello mushrooms weighing about 7.6mg will provide you with close to 40% of your daily niacin needs.
One cup of cooked white mushrooms will provide you 35%, Oyster raw mushrooms will give you 21%, brown raw will give 14% and Chanterelle when eaten raw will give 11%.
In addition to this, mushrooms are chock full of other nutrients that are beneficial to your health.
Liver:
3 ounces of cooked liver will provide you with about 71% of your daily niacin needs. This number may vary slightly depending on which type of liver you choose to use.
Green peas:
Green peas are another great source of niacin. One raw cup of green peas will provide you with about 15% of your daily niacin needs.
Frozen peas will provide you with 12% of your niacin needs while a cup of canned peas will provide you with about 8% only.
Brown rice:
1 cup of brown rice will provide you with 19% of your daily recommended intake of niacin. White rice however, because of the processes it has gone through will give very little to no niacin when it is digested.
Other carbohydrates such as sweet potatoes, potatoes, corn and beans will give between 11 and 19% of your niacin daily recommendation.
Sardines:
3 ounces of sardines will give up to 30% of the daily recommendation of niacin for your body for just 190 calories. Sardines in tins have a little less niacin than fresher options.
Shrimp:
4 ounces of shrimp will produce about 19% of the daily recommendations for niacin when eaten. Other seafood like prawn, squid and fish have great quantities of niacin as well.
Avocado:
Avocado is a great source of niacin and numerous other nutrients. Its year round availability doesn’t hurt either. One avocado eaten whole can give as much as 17% of the recommended niacin intake in a day.
Other great sources of niacin are beets, brewer’s yeast, etc.
Benefits
There are several benefits to eating adequate amounts of niacin daily.
Moderation of Cholesterol levels:
Niacin has been found to reduce the presence of bad cholesterol and increase the good cholesterol found in our bodies.
The presence of excessive quantities of bad cholesterol is a risk factor for heart disease and can lead to other unpleasant side effects.
Improvement of Cardiovascular Health:
Heart health can be improved by niacin. The action of reducing the bad cholesterol in our bodies can on its own lead to an improvement in heart health.
A reduction in cholesterol means that your heart will no longer have to work extra hard to pump blood through narrow blood vessels.
Healthier Skin:
Niacin is one of the few vitamins that can have a positive direct effect on how the skin looks. While some people may experience a niacin flush when they take niacin, others may not.
Regardless of whether you experience a flush or not, niacin will improve the appearance of your skin by improving blood flow, reducing bad cholesterol and improving the health of your nervous system.
Increase in Energy:
Niacin is able to directly affect the pathways that determine the breakdown of fats, protein and carbohydrates to form energy.
This happens because the enzymes NAD and NADP are made unique forms of vitamin B3. Because of this action, adequate niacin levels are also necessary for fat loss.
Healthier Nervous System:
Niacin also improves the health of the nervous system. Niacin in the form of NAD is necessary for the functioning of several pathways in the nervous system.
Antioxidant Function:
NAD and NADP are beneficial to the reduction of free radicals in the body. The presence of free radicals can cause excessive damage to living tissue and lead to more serious health problems.
Hormone Production
Niacin is involved in the production of various sex and stress hormones in the body.
Niacin may help with Alzheimer’s, osteoarthritis, type 1 diabetes, cataracts and even reduce the risk of subsequent strokes in stroke sufferers.
Risk and Effects of Niacin Deficiency
A deficiency of niacin can lead to several conditions. These include;
- Pellagra:
Pellagra is a disease condition caused by a deficiency of nicotinic acid. Its symptoms include diarrhea, dizziness, vomiting and mental disturbance. Treating pellagra will involve medication and dietary modification for optimum results.
- Indigestion:
Vitamin B3 is essential to the digestion of carbohydrates, fat and protein to produce energy. It is involved in the production of NAD and NADP.
These are enzymes that regulate pathways in the gut and determine the rate at which digestion occurs. Deficiency of these enzymes will lead to indigestion and poor neural function.
- Fatigue:
When a deficiency of vitamin B3 occurs, there is resulting fatigue. This occurs because the macronutrients that should be broken down to give energy will remain in the digestive path for a long time. When no energy is produced, fatigue sets in.
Other symptoms of a vitamin B3 deficiency are canker sores, vomiting, poor circulation and depression.
Risk of Excess Niacin Intake
Even though niacin is good for the health, excess consumption of niacin can lead to a variety of symptoms.
It is not possible to overdose on niacin by eating too many niacin rich foods. However, it is possible to do so if you use niacin medication.
These symptoms include;
- Severe skin flushing combined with dizziness
- Rapid heartbeat
- Itching
- Nausea and vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Diarrhea
- Gout
Conclusion
In conclusion, niacin is an important part of a heart healthy diet and is beneficial to your nervous system and overall well-being.
For best results when using niacin supplements, take only as much niacin as is recommended and do not exceed the stipulated dosage.



Post Comment